

To get started with Gradle for this tutorial, begin by downloading the materials at the top or bottom of the page using the Download materials button. It will allow you to pass flags to your code, manage dependencies, and it supports pre- and post-processing your build outputs. Apart from these features, Gradle is highly customizable. All of this makes sure build times are small, in most cases. Gradle supports incremental builds, makes intelligent decisions to skip building up-to-date dependencies and makes use of caching at multiple stages. Recently, a Kotlin-based DSL for Gradle has also become an option. It uses a Groovy-based domain-specific language (DSL) instead of the common XML for declaring project configurations in other build systems in the Java ecosystem.

Gradle is an open-source build automation system. Other prerequisites include knowledge of using the Bash shell, the Terminal and Android Studio 3.1 or later. If you are new to the Gradle build system, also check out Gradle Tutorial for Android: Getting Started. If you’re new to Android Development, it’s highly recommended that you work through Beginning Android Development and Kotlin for Android to learn about the basic tools and concepts. This Gradle tips-and-tricks tutorial assumes that you know the basics of Android development and working with Gradle. Groovy is widely used and is also the default in Android Studio out of the box.
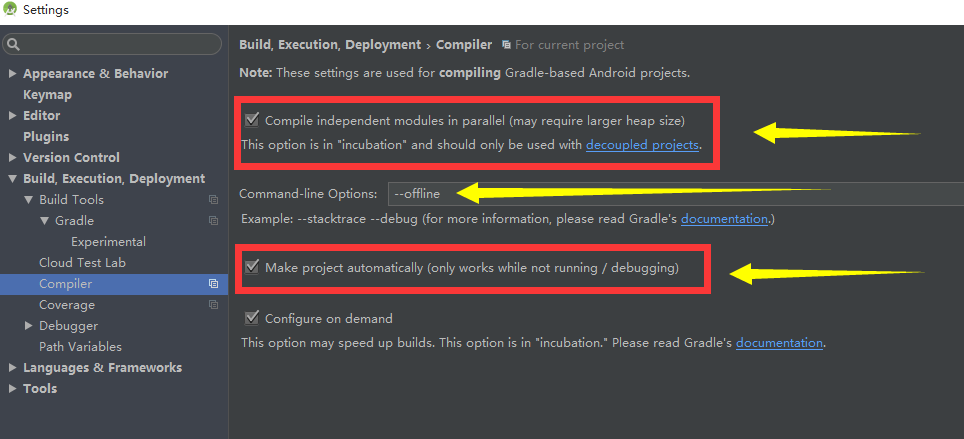
Note: You typically will use Groovy for writing your Gradle build files.

From taking care of complex tasks to making sure all tests have passed while you spend time writing new features and crushing bugs in your codebase. The current state of build automation tools handles several aspects of building a project more efficiently than in the past. Gone are the days when you will be having a cup of coffee and browsing the Internet just after you have started the build for your Android project because it takes ages to complete - or having to fiddle with customizing your build system. Learn some cool tricks for working with the Gradle build system, such as autocompletion, using build-time variables, and reducing build time!


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
